Clerk module¶
Preliminary terminology¶
- A
StateSenderis a contract deployed on L1 (Ethereum) responsible for emitting state-sync events. - A
StateReceiveris a contract deployed on L2 (Bor) responsible for receiving state-sync events. - A
EventRecordis a record of the state-sync event stored in the heimdall state.
Overview¶
Clerk module manages generic event records from the Ethereum blockchain related to state-sync events.
These are specially designed events that are emitted by the StateSender contract on the L1 chain to notify the L2 nodes
(Bor in case of PoS) about the state changes in the L1.
Once the bridge processes the events,
the clerk module listens to these events and stores them in the database for further processing.
State-Sync Mechanism¶
It’s a mechanism for state-management between the Ethereum and Bor chain. The events generated are called state-sync events. This is a way to move data from the L1 chain to the L2 chain.
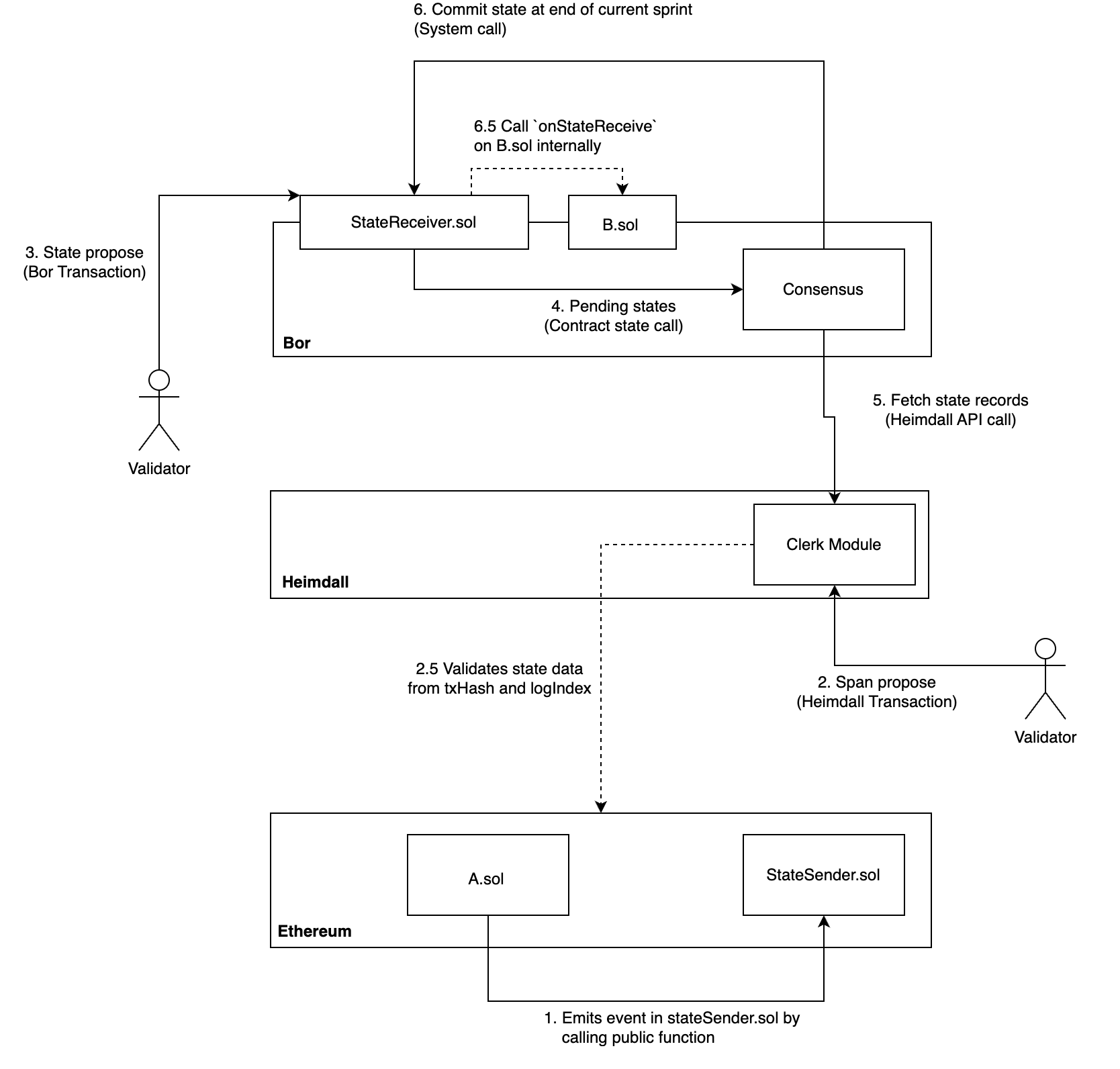
How it works¶
An EventRecord is defined by the data structure :
message EventRecord {
option (gogoproto.goproto_getters) = false;
option (gogoproto.equal) = false;
uint64 id = 1 [ (amino.dont_omitempty) = true ];
string contract = 2 [
(amino.dont_omitempty) = true,
(cosmos_proto.scalar) = "cosmos.AddressString"
];
bytes data = 3 [ (amino.dont_omitempty) = true ];
string tx_hash = 4 [ (amino.dont_omitempty) = true ];
uint64 log_index = 5 [ (amino.dont_omitempty) = true ];
string bor_chain_id = 6 [ (amino.dont_omitempty) = true ];
google.protobuf.Timestamp record_time = 7 [
(gogoproto.stdtime) = true,
(gogoproto.nullable) = false,
(amino.dont_omitempty) = true
];
}
idis the unique identifier for the event record, Generated by theStateSendercontract.contractis the address of the contract on the L2 chain on which the event will be processed.datais the data of the event which will be processed by the contract.txHashis the transaction hash of the event on the L1 chain.logIndexis the log index of the event on the L1 chain.borChainIDis the chain id of the bor chain.recordTimeis the time at which the event was recorded in heimdall state.
The bridge will listen to the state-sync events from L1 and generate a txn with MsgEventRecord which is responsible for validating events from StateSender contract and storing the EventRecord on the heimdall state for bor to use.
message MsgEventRecord {
option (amino.name) = "heimdallv2/clerk/MsgEventRecord";
option (gogoproto.equal) = false;
option (gogoproto.goproto_getters) = false;
option (cosmos.msg.v1.signer) = "from";
string from = 1 [
(amino.dont_omitempty) = true,
(cosmos_proto.scalar) = "cosmos.AddressString"
];
string tx_hash = 2 [ (amino.dont_omitempty) = true ];
uint64 log_index = 3 [ (amino.dont_omitempty) = true ];
uint64 block_number = 4 [ (amino.dont_omitempty) = true ];
string contract_address = 5 [
(amino.dont_omitempty) = true,
(cosmos_proto.scalar) = "cosmos.AddressString"
];
bytes data = 6 [ (amino.dont_omitempty) = true ];
uint64 id = 7 [ (amino.dont_omitempty) = true ];
string chain_id = 8 [ (amino.dont_omitempty) = true ];
}
Handler for this transaction validates for multiple conditions including TxHash and LogIndex to ensure that the event exists on L1 and the data is not tampered with, It throws Older invalid tx found error if the event is already processed.
Once the event is validated by the Handler,
it will go to SideHandleMsgEventRecord in each validator node and after verifying the event,
the validators will vote with either a YES return an error for failed verification.
Only when there is a majority of YES votes, The event will be processed by PostHandleMsgEventRecord which will persist the event in the state via keeper.
How to add an event¶
A validator can leverage the CLI to add an event to the state in case it’s missing and not processed by the bridge, The CLI command is :
heimdalld tx clerk handle-msg-event-record [from] [tx-hash] [log-index] [block-number] [contract-address] [data] [id] [chain-id]
Query commands¶
One can run the following query commands from the clerk module :
record- Query for a specific event record by its ID.record-list- Query a list of event records by page and limit.is-old-tx- Query if the event record is already processed.latest-record-id- Query the latest record (state-sync) id from L1.
CLI commands¶
heimdalld query clerk record [record-id]
heimdalld query clerk record-list [page] [limit]
heimdalld query clerk record-list-with-time [from-id] [to-time]
heimdalld query clerk record-sequence [tx-hash] [log-index]
heimdalld query clerk is-old-tx [tx-hash] [log-index]
heimdalld query clerk latest-record-id
GRPC Endpoints¶
The endpoints and the params are defined in the clerk/query.proto file. Please refer to them for more information about the optional params.
grpcurl -plaintext -d '{}' localhost:9090 heimdallv2.clerk.Query/GetRecordList
grpcurl -plaintext -d '{"record_id": <>}' localhost:9090 heimdallv2.clerk.Query/GetRecordById
grpcurl -plaintext -d '{}' localhost:9090 heimdallv2.clerk.Query/GetRecordListWithTime
grpcurl -plaintext -d '{"tx_hash": <>, "log_index": <>}' localhost:9090 heimdallv2.clerk.Query/GetRecordSequence
grpcurl -plaintext -d '{"tx_hash": <>, "log_index": <>}' localhost:9090 heimdallv2.clerk.Query/IsClerkTxOld
grpcurl -plaintext -d '{}' localhost:9090 heimdallv2.clerk.Query/GetLatestRecordId
REST endpoints¶
The endpoints and the params are defined in the clerk/query.proto file. Please refer to them for more information about the optional params.
curl localhost:1317/clerk/event-records/list?page=<page>&limit=<limit>
curl localhost:1317/clerk/event-records/latest-id
curl localhost:1317/clerk/event-records/<event-id>
curl localhost:1317/clerk/time?from_id=<from-id>&to_time=<to-time>&page=<page>&limit=<limit>
curl localhost:1317/clerk/sequence?tx_hash=<tx-hash>&log_index=<log-index>
curl localhost:1317/clerk/is-old-tx?tx_hash=<tx-hash>&log_index=<log-index>